The New Generation Rollingstock (NGR) project is an A$4.4bn ($4.1bn) project aimed at adding 75 six-car trains to the rail network in South East Queensland, Australia, by 2018. The introduction of new trains is expected to increase the network’s overall fleet size by 30%.
Queensland’s single biggest ever investment in rail infrastructure also includes the construction of a maintenance centre at Wulkuraka, near Ipswich, and three NGR training simulators for train crew.
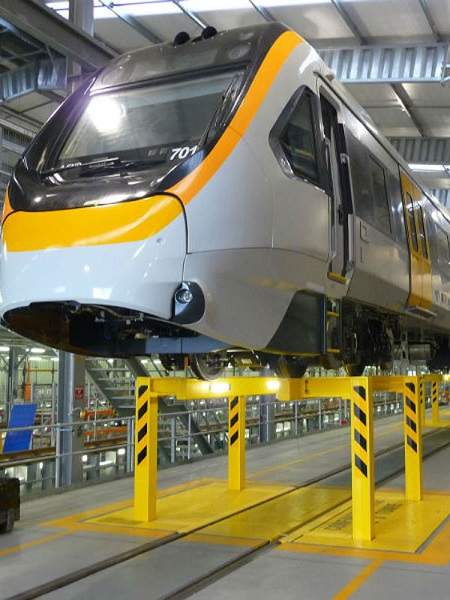
On-track testing of the first NGR trains started at the maintenance centre in September 2016. The NGR trains are expected to start services in 2017, while the complete fleet will be operational by late-2018.
To be operated by Queensland Rail, the NGR trains will initially run on the high-demand Airport and Gold Coast line. The train services will be useful for the 2018 Gold Coast Commonwealth Games.
Being delivered under an availability public-private partnership (PPP) agreement, the project is expected to create approximately 500 full-time jobs and up to 1,500 indirect jobs.
Details of the Queensland rolling stock
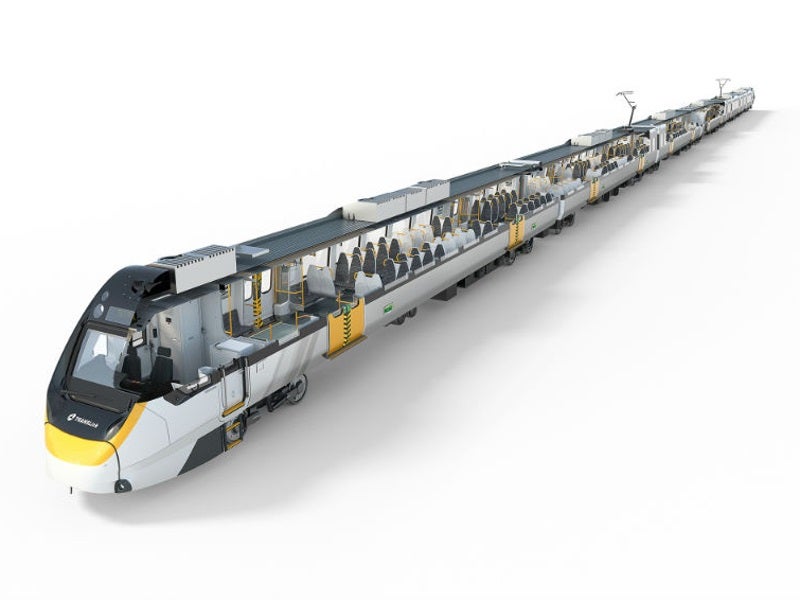
The new six-car electrical multiple units (EMUs) are designed in Queensland and will be assembled at Bombardier’s facility in Savli, India. The assembled trains will be shipped by a cargo vessel to the Port of Brisbane, where they will be unloaded and hauled to the NGR Maintenance Centre to undergo further testing before commencing services.
The design of the new trains is based on the Adelaide EMU train and the Bombardier VLocity models. The trains will be equipped with advanced technologies such as Bombardier FLEXX bogies and the MITRAC propulsion system.
Each 147m-long NGR train will weigh approximately 260t. The trains can accommodate 964 people, including 454 seated and 510 standing.
The trains will have longer aerodynamic noses on the front and rear cars thereby surrounding the train coupler completely. It will also comprise a smooth-sided exterior with matte finish, in addition to high-backed seats for improved crash safety performance.
Details of the Wulkuraka maintenance centre
Construction works on the Wulkuraka maintenance centre were started in April 2014 and the facility was officially opened in February 2016. The Centre will employ roughly 150 full-time staff to service and maintain the NGR fleet, which will be progressively rolled out onto the network until late-2018.
The site comprises ten railroads, six of which lead to the maintenance centre, one wash bay, four service bays, and one for train jacking consisting of specialist equipment that can lift a whole 200t train off the rails.
Other components of the centre include a wheel lathe building, stabling yards, a drivers’ facility, catering and administration offices.
As part of the maintenance centre construction, a number of other local works were also conducted around Wulkuraka to connect it to the local road and rail network. The works included the construction of a new rail line section, storm water civil works, infrastructure facilities, and widening and resurfacing of Dixon St East.
Opened in December 2015, a new pedestrian footbridge was also constructed as part of the other works near the maintenance centre.
Testing of the new-generation rolling stock
A comprehensive testing and commissioning program will be undertaken to ensure the operational safety of the trains. The trains will undergo static testing and information and communications technology (ICT) test to check the compatibility of the on-board equipment with the existing Queensland rail systems.
On-track testing of the NGR trains is being conducted around the South East Queensland passenger rail network.
Train safety and monitoring system
The new commuter trains offer increased vehicle reliability with the installation of the BOMBARDIER ORBIFLO advanced condition monitoring system.
The trains also have the option for future installation of the European Train Control System (ETCS), an automatic train protection system.
Financing
Financial closure of the project was achieved in January 2014. The project is funded jointly by the public and private sector through an availability payment PPP finance option, a similar method followed for Australia’s Gold Coast Rapid Transit.
Four Japanese banks, namely Mizuho Bank; Shinsei Bank; Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Bank; and Aozora Bank, provided the financing.
Equity funding is being provided by the four consortium members, with Macquarie Capital being the financial adviser.
Key players involved with the NGR project
The Department of Transport and Main Roads is delivering the project in partnership with Projects Queensland. Queensland Rail is responsible for the technical expertise required for integrating the new trains with the existing network.
Qtectic, a consortium between Bombardier Transportation, John Laing, Itochu, and Aberdeen Infrastructure Investments, was awarded the contract for the NGR project in December 2013. The contractual scope includes design, construction and maintenance of the NGR trains, design and construction of the maintenance centre, as well as the procurement of three training simulators.
As part of the consortium, Bombardier is responsible for the supply of the 75 EMUs and their maintenance for 30 years.
Laing O’Rourke was engaged for the design and construction of the Wulkuraka maintenance centre. Arcadis prepared the detailed design of the maintenance centre by using 3D building information modelling (BIM) method.






